SAT: Spatial aptitude training for multimodal language models
Arijit Ray, Jiafei Duan, Reuben Tan, Dina Bashkirova, Rose Hendrix, Kiana Ehsani, Aniruddha Kembhavi, Bryan A Plummer, Ranjay Krishna, Kuo-Hao Zeng, Kate Saenko
[COLM 2025]: Simulated spatial aptitude data (SAT) can improve spatial reasoning in real images and videos for MLMs while maintaining pretraining commonsense. When instruction-tuned on SAT, LLaVA-13B outperforms some larger MLMs like GPT4-V and Gemini-1.5-pro in spatial reasoning.
Lasagna: Layered Score Distillation for Disentangled Object Relighting
[NeurIPS 2023 Workshop]: We propose Lasagna, a layered image editing approach that allows controlled and language-guided object relighting. Lasagna achieves a controlled relighting via layered score distillation sampling that allows extracting the diffusion model lighting prior without changing other crucial aspects of the input image.
Dina Bashkirova, Arijit Ray, Rupayan Mallick, Sarah Adel Bargal, Jianming Zhang, Ranjay Krishna, Kate Seanko
At the core of image and video translation and editing tasks lies the problem of preserving the semantics of the given input visual content. In this thesis, we explore semantic consistency in various image and video editing tasks, including image translation, stylization, relighting, and even semantic segmentation. We propose a formal definition of semantic consistency through the lens of disentanglement, and analyze popular editing approaches in term of both editing quality and semantic consistency.
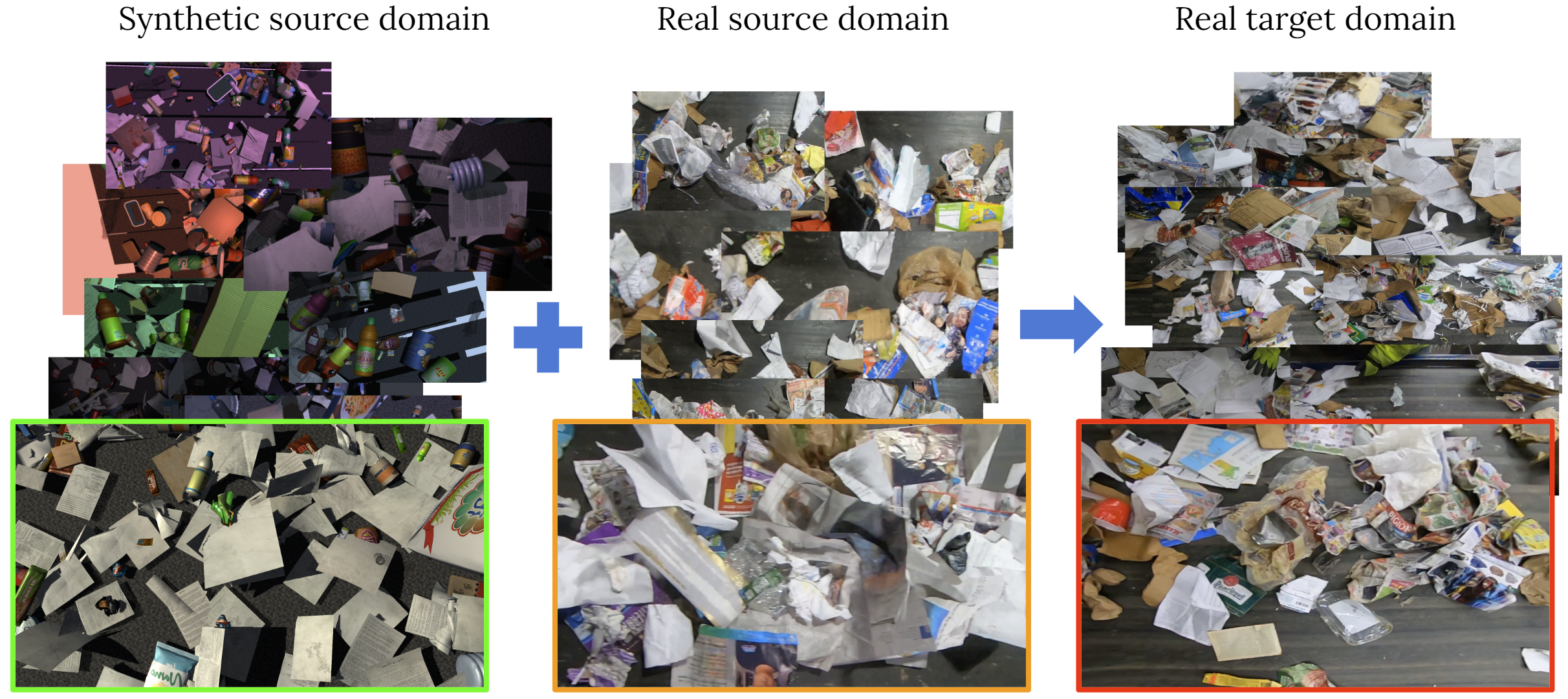
VisDA 2022 challenge: Domain adaptation for industrial waste sorting
Dina Bashkirova, Samarth Mishra, Diala Lteif, Piotr Teterwak, Donghyun Kim, Fadi Alladkani, James Akl, Berk Calli, Sarah Adel Bargal, Kate Saenko, Daehan Kim, Minseok Seo, YoungJin Jeon, Dong-Geol Choi, Shahaf Ettedgui, Raja Giryes, Shady Abu-Hussein, Binhui Xie, Shuang Li
[NeurIPS 2023 Competition]: We propose Lasagna, a layered image editing approach that allows controlled and language-guided object relighting. Lasagna achieves a controlled relighting via layered score distillation sampling that allows extracting the diffusion model lighting prior without changing other crucial aspects of the input image.
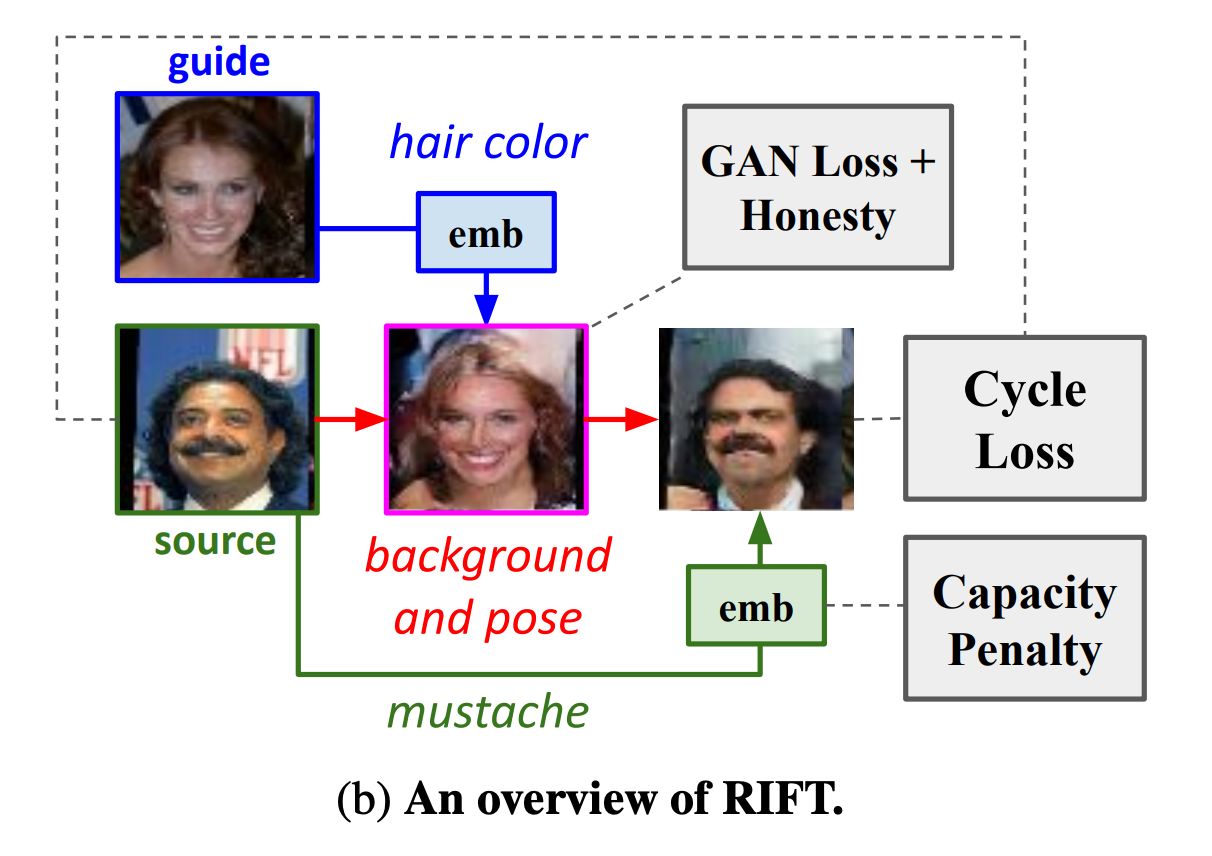
RIFT: Disentangled unsupervised image translation via restricted information flow
Ben Usman, Dina Bashkirova, Kate Saenko
[WACV 2023]: In this paper, we show that many state-of-the-art architectures implicitly treat textures and colors as always being domain-specific, and thus fail when they are not. We propose a new method called RIFT that does not rely on such inductive architectural biases and instead infers which attributes are domainspecific vs shared directly from data. As a result, RIFT achieves consistently high cross-domain manipulation accuracy across multiple datasets spanning a wide variety of domain-specific and shared factors of variation.
MaskSketch: Unpaired structure-guided masked image generation
Dina Bashkirova, Jose Lezama, Kihyuk Sohn, Kate Saenko, Irfan Essa
[CVPR 2023 Highlight]: We introduce MaskSketch, an image generation method that allows spatial conditioning of the generation result using a guiding sketch as an extra conditioning signal during sampling. MaskSketch uses a pre-trained masked generative transformer, requiring no model training or paired supervision, and works with input sketches of different levels of abstraction. We show that intermediate self-attention maps of a masked generative transformer important structural information of the input image, such as scene layout and object shape, and we propose a novel sampling method based on this observation to enable structure-guided generation.
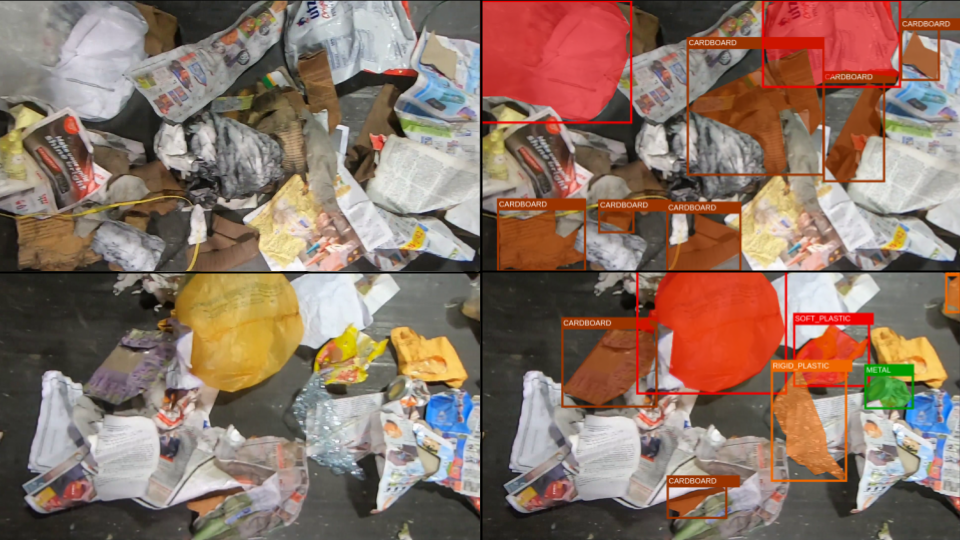
ZeroWaste Dataset: Towards Deformable Object Segmentation in Cluttered Scenes
Dina Bashkirova, Mohamed Abdelfattah, Ziliang Zhu, James Akl, Fadi Alladkani, Ping Hu, Vitaly Ablavsky, Berk Calli, Sarah Adel Bargal and Kate Saenko
[CVPR 2022]: In this paper, we take a step towards computer-aided waste detection and present the first in-the-wild industrial-grade waste detection and segmentation dataset, ZeroWaste. We demonstrate that state-of-the-art segmentation and object detection methods fail on this challenging waste object detection benchmark.
Adversarial Self-Defense for Cycle-Consistent GANs
Dina Bashkirova, Ben Usman, Kate Saenko
[NeurIPS 2019]: In this paper, we show that cycle consistency loss commonly used in image translation methods causes the translation model to hide the information about it’s input in a form of inperceptible high-frequency structured noise in order to perfectly reconstruct it. We further show that such behavior is detrimental to preserving the input image semantics, and propose an alternative self-adversarial loss that prevents the information hiding, and therefore significantly improves the semantic alignment.
Unsupervised Video-to-Video Translation
Dina Bashkirova, Ben Usman, Kate Saenko
[2018]: In this paper, we extend the popular image-to-image translation method, CycleGAN, to video translation application. We show that joint video frame translation results in improved alignment across the resulting frames compared to per-frame translation.
Fast L1 Gauss transforms for edge-aware image filtering
Dina Bashkirova, Shin Yoshizawa, Rustam Latypov, Hideo Yokota
[ISP RAS 2017]: In this paper, we propose a novel approximation method for fast Gaussian convolution of two-dimensional uniform point sets, such as 2D images. Our method employs L1 distance metric for Gaussian function and domain splitting approach to achieve fast computation (linear computational complexity) while preserving high accuracy. Our numerical experiments show the advantages over conventional methods in terms of speed and precision.